HIVE is a Data warehouse, it is not a database.
Like how important it is to understand when to use a particular tool, it is equally important to understand when NOT to use it.
- HIVE is designed for only analytical operations in large scale, it is not a good fit for transactional operations.
- HIVE data is totally de-normalized.
- HIVE supports JOINS but need to avoid them as much as we can to improve performance.
- HIVE query language HQL is similar to SQL.
Lets understand the relation between Hadoop and HIVE :
- HDFS is having folders and files
- HIVE have databases and tables
- When we create a database in HIVE, it will create a folder in HDFS
- When we create a table in HIVE, it will create a folder in HDFS
- When we insert records in HIVE table, those records will be saved in HDFS in the form of files
- Delimiter is very important while creating a table in HIVE
- Delimiter can be a Comma, Tab etc.,
- HIVE can store structured, semi-structured & un-structured data but it is important to convert un-structured data into HIVE understandable format using serDe, we will see more about it in further blogs of HIVE
Table in HIVE How it sore in HDFS as a file
C1 C2 C3 11,12,13
11 12 13 21,22,23
21 22 23
Always write your HIVE queries in a notepad and copy paste them in HIVE prompt because HIVE won't allow you to update the query if there is a mistake.
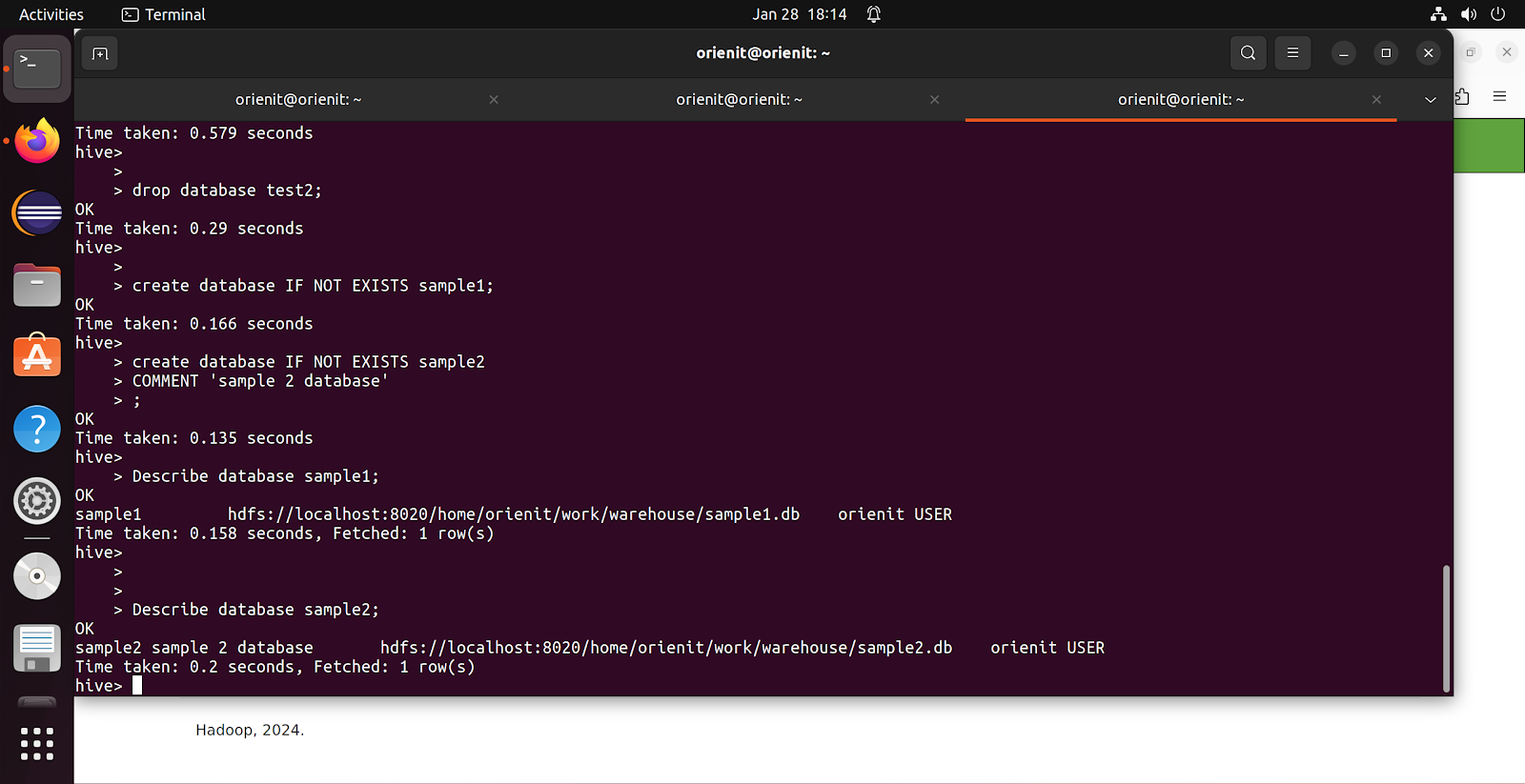
Create a Database in HIVE :
Syntax 1 :
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS <DB_NAME>;
Syntax 2 :
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS <DB_NAME>
COMMENT 'COMMENT ON DATABASE'
LOCATION 'PATH OF THE DATABASE LOCATION'
WITH DBPROPERTIES(KEY1 = VALUE1, KEY2 = VALUE2,….)
;
Location path should be a folder, it won't work if it is a file path. Because in HIVE table will be saved as folder and records will be saved as file.
We can also add some properties as shown below :
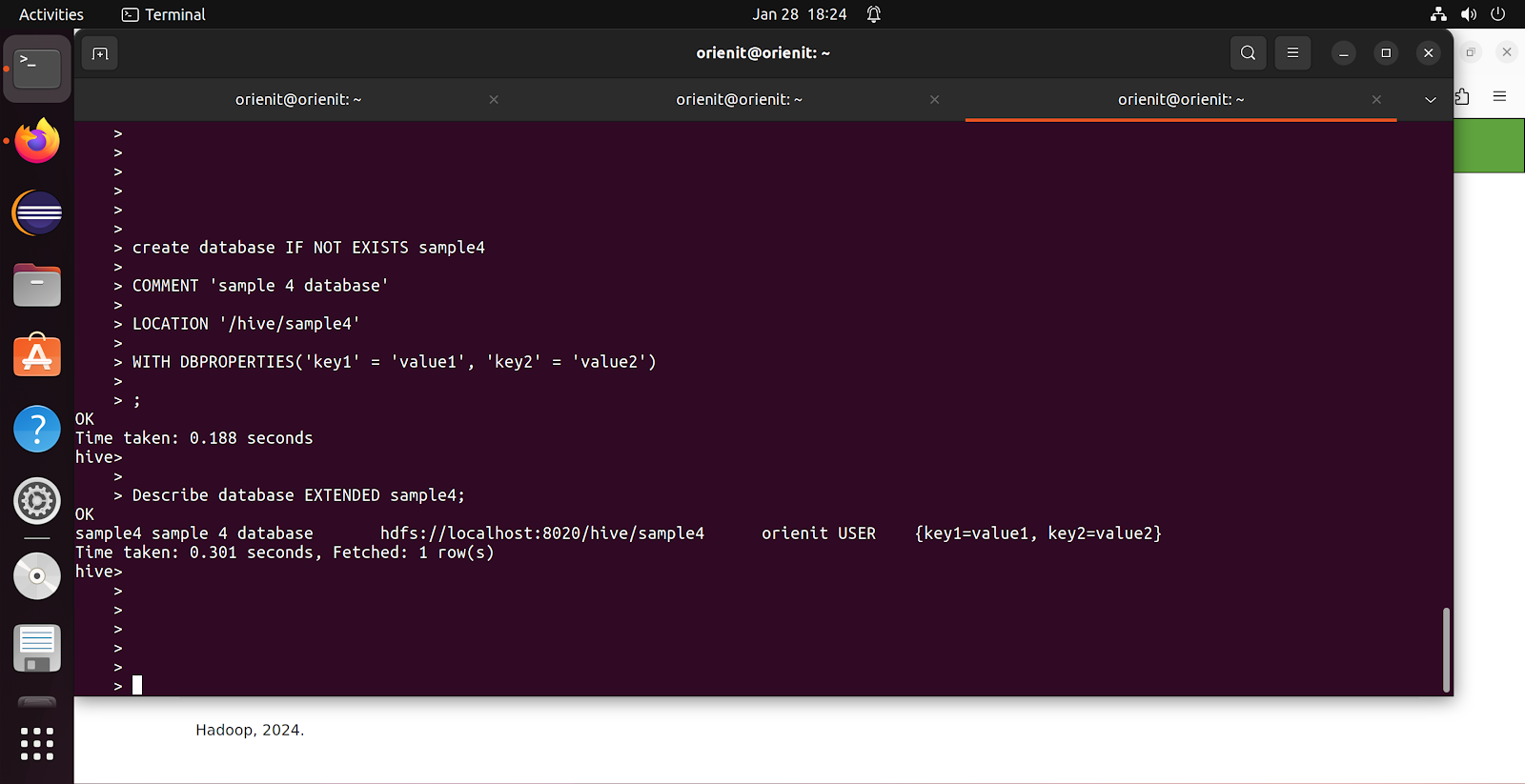
Example :
create database IF NOT EXISTS sample4
COMMENT 'sample 4 database'
LOCATION '/hive/sample4'
WITH DBPROPERTIES('key1' = 'value1', 'key2' = 'value2')
;
These properties will be useful while working with other systems like Spark, and other NoSQL databases to send them some access information.
Using EXTENDED keyword while describing a database will print additional information as well like key, value information which we have used in above WITH DBPROPERTIES keyword while creating sample4 database.
Describe database EXTENDED sample4;
Note :
- WHEN WE CREATE A DATABASE / TABLE LOCATION PATH MUST & SHOULD BE FOLDER PATH, NOT FILE PATH
- IF FOLDER PATH EXISTS, THEN IT WILL USE IT
- IF FOLDER PATH NOT EXISTS, THEN IT WILL CREATE IT
- IF FILE PATH EXISTS, THEN IT THROW AN ERROR
DROP DATABASE in HIVE :
Syntax :
- DROP DATABASE <DATABASE_NAME>;
- DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS <DATABASE_NAME>;
- DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS <DATABASE_NAME>;
- DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS <DATABASE_NAME> RESTRICT;
- DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS <DATABASE_NAME> CASCADE;
Examples :
- DROP database IF EXISTS sample1;
- DROP database IF EXISTS sample1 RESTRICT; ==> It will restrict to drop a database if it is having some tables in it
- DROP database IF EXISTS sample1 CASCADE; ==> This is like a force drop, it will drop database though there are tables associated to this database sample1
We will see more about creating tables in next blog. Have a great day!
Arun Mathe
Gmail ID : arunkumar.mathe@gmail.com

Comments
Post a Comment